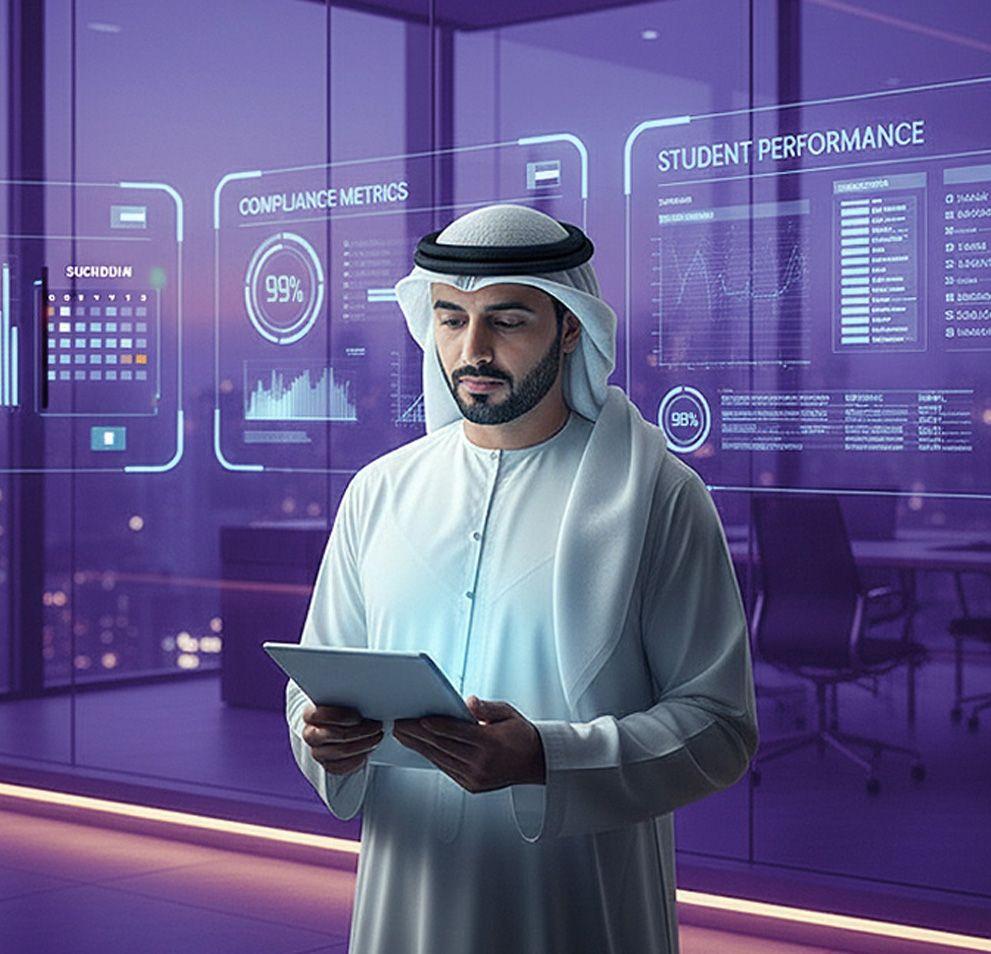
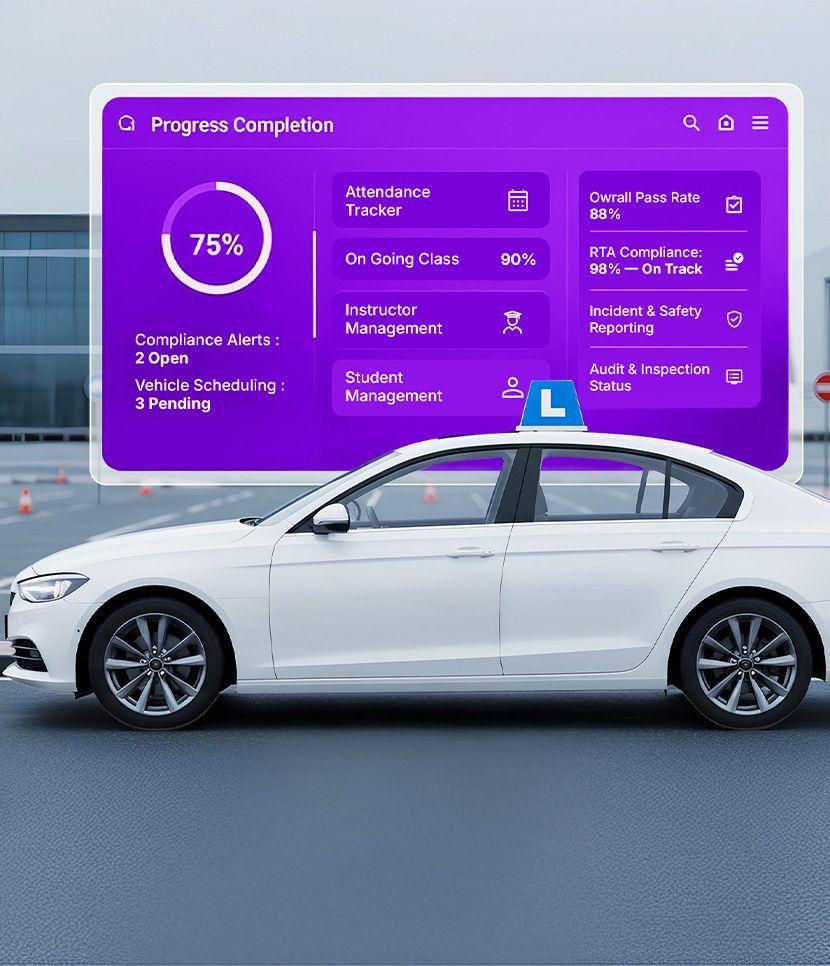
Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility Transforming global driver training and licensing with AI-powered driver training software by connecting students, instructors, driving centres, and regulators in a seamless ecosystem.
Empowering all Stakeholders with Pedal Mobilitys Solutions.
Driving the Future With Results That Matter
Empowering students worldwide with innovative driver training software solutions tailored for modern learning.
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
Maximizing efficiency by smartly assigning vehicles and instructors, driven by our centralized driving school system.
Going fully digital with a paperless, user-friendly onboarding system powered by modern driving software.
Engaging students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility
Pedal transforms driver education by integrating AI and automation into every step. Our centralized driving training software connects students, instructors, and regulators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem built for modern mobility.
Insights and Stories shaping Driver Education
From instructor management to vehicle assignment, we are driving the future with results that matter.
Our platform connects students, instructors, and training admins every day through a connected, seamless, and intuitive driver training platform.
Introducing the New Era of AI in Personal Mobility